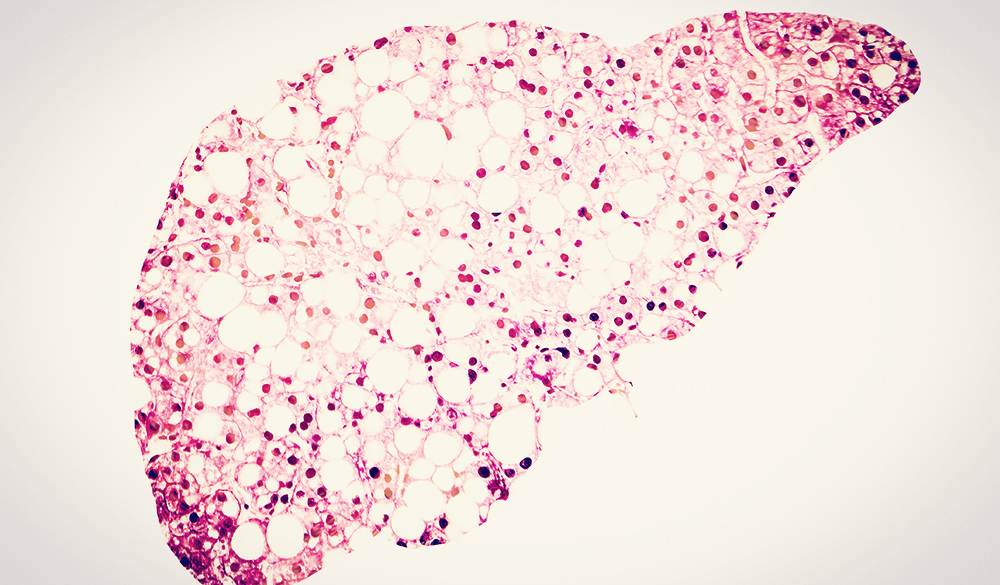
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterised by excess lipids in hepatocytes due to an overload of fatty acid influx from adipose tissue, as well as the consumption of too many dietary fats and carbohydrates. Untreated NAFLD and the subsequent mitochondrial oxidative stress and cellular damage it causes can potentially result in non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis (NASH) - a more severe liver disease that can progress into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Copper has recently come into the spotlight for potential use as part of the solution to a lack of pharmacological interventions approved for NAFLD treatment due to its antioxidant capacities produced by copper-binding compounds.
Oxidative stress plays a major role in the progression of NAFLD, which seems to be the most important component leading to hepatic injury. Copper is one of the main bio-metals required for physiological redox reactions, which primarily occurs during mitochondrial respirations. It is suggested that dysregulation of copper homeostasis may play a part in NAFLD progression due to the alteration in oxidative capacity of copper-binding compounds including curcurmin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), luteolin, caffeic acid, caffeine, oleuropein, quercetin, rutin, and resveratrol.
The study highlights the importance of copper homeostasis and the requirement for further research to be conducted on the many antioxidant compounds that bind to copper for their natural abilities to assist management of NAFLD and prevent severe disease progression.
Reference
- Antonucci L, Porcu C, Iannuci G, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and nutritional implications: special focus on copper. Nutrients 2017;9(10):1137.
DISCLAIMER:
The information provided on FX Medicine is for educational and informational purposes only. The information provided on this site is not, nor is it intended to be, a substitute for professional advice or care. Please seek the advice of a qualified health care professional in the event something you have read here raises questions or concerns regarding your health.