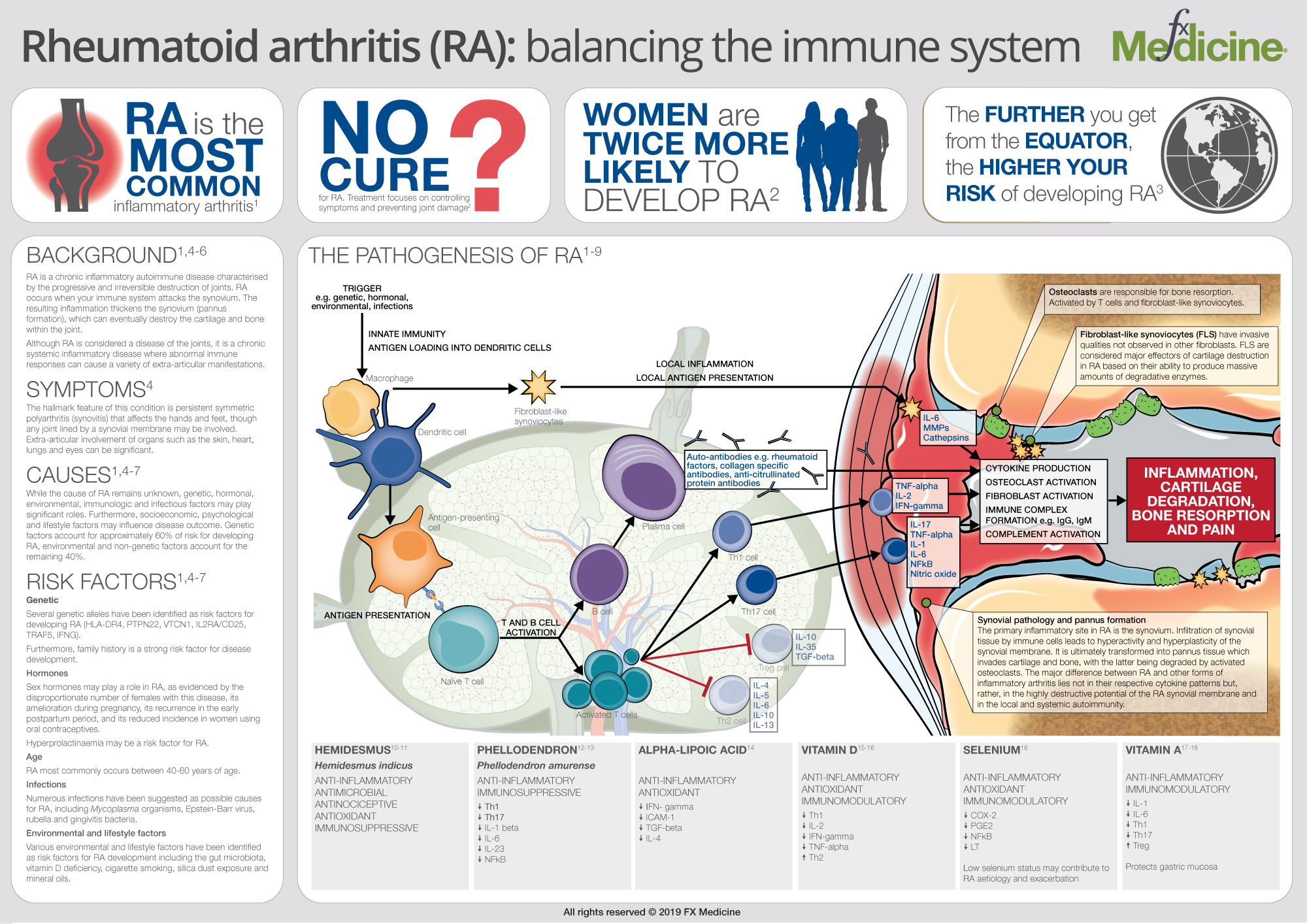
Rheumatoid arthritis is a serious autoimmune disease that causes pain, inflammation and deformity of the joints. Eventually, this inflammation may lead to degeneration of the cartilage causing bone to be worn away. The exact causes for RA aren’t fully understood, but there do seem to be a number of factors involved.
While genetics certainly seems to play a key role, it is the combination of stress, environmental and lifestyle factors that determine the likelihood of developing the disease. These factors include infectious agents such as bacteria or viruses, hormones, obesity, physical or emotional trauma, cigarette smoke and air pollution.
Conventional treatment typically involves a variety of drugs that potentially have serious side effects, including NSAIDs, steroids, and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These are often prescribed, starting with those drugs that have the fewest side effects, but the use of stronger drugs or combinations of drugs is common as the disease progresses. Certain nutrient compounds and herbal medicines have also been demonstrated to benefit RA patients through a variety of immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects.
In this infographic we focus on some of the triggers of this disease and explore underlying immunological processes. We also look at some of the encouraging alternative options for treatment that may significantly improve the long-term outcome for patients, with little or no side-effects.
References
- Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, et al. Kelley’s textbook of rheumatology, 9th ed. Philidelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2012.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Mayo Clnic 2015. Viewed 6 October 2015, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/basics/definition/con-20014868
- Vieira VM, Hart JE, Webster TF, et al. Association between residences in U.S. northern latitudes and rheumatoid arthritis: a spatial analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study. Environ Health Perspect 2010;118(7):957-961. [Full text]
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Medscape 2015. Viewed 6 October 2015, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/331715-overview#a2
- Maciejewska Rodrigues H, Jüngel A, Gay RE, et al. Innate immunity, epigenetics and autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol 2009;47(1):12-18. [Abstract]
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Mayo Clinic 2015. Viewed 6 October 2015, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/basics/risk-factors/con-20014868
- Environmental risk factors. RheumatoidArthritis.net. Viewed 6 October 2015, http://rheumatoidarthritis.net/causes/environmental-risk-factors/
- Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immun Rev 2010;233(1):233-255. [Full text]
- Mackay CR. CXCR3+CCR5+ T cells and autoimmune diseases: guilty as charged? J Clin Invest 2014;124(9):3682–3684. [Full text]
- Das S, Bisht SS. The bioactive and therapeutic potential of Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. (Indian sarsaparilla) root. Phytother Res 2013;27(6):791-801. [Abstract]
- George S, Tushar KV, Unnikrishnan KP, et al. Hemidesmus indicus (L.) R. Br. A review. J Plant Sc 2008;3(2):146-156. [PDF]
- Qin X, Guo BT, Wan B, et al. Regulation of Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation and amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by natural product compound berberine. J Immunol 2010;185(3):1855-1863. [Full text]
- Yang Y, Qi J, Wang Q, et al. Berberine suppresses Th17 and dendritic cell responses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013;54(4):2516-2522. [Full text]
- Khalili M, Azimi A, Izadi V, et al. Does lipoic acid consumption affect the cytokine profile in multiple sclerosis patients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014;21(6):291-296. [Abstract]
- Lin, The pleiotropic actions of vitamin D. Bioassays 2004;26(1):21-28. [Abstract]
- Braun L, Cohen M. Herbs and natural supplements: an evidence-based guide, 4th ed. Sydney: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2015.
- Mora JR, Iwata M, von Andrian UH. Vitamin effects on the immune system: vitamins A and D take centre stage. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):685-698. [Full text]
- Lu L, Lan Q, Li Z, er al. Critical role of all-trans retinoic acid in stabilizing human natural regulatory T cells under inflammatory conditions. Proc Natl Sci U S A 2014;111(33):E3432-3440. [Full text]
This image by FX Medicine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
More information about how to share/use the infographics for personal use.
If you interested in using any FX Medicine content for commercial use please contact us.
DISCLAIMER:
The information provided on FX Medicine is for educational and informational purposes only. The information provided on this site is not, nor is it intended to be, a substitute for professional advice or care. Please seek the advice of a qualified health care professional in the event something you have read here raises questions or concerns regarding your health.




