Dr. Lily Tomas explores the complexities of fibromyalgia including chronic inflammation, risk factors, and the role of mitochondria, mast cells, microglia, and the brain.
Dr. Lily Tomas explores the complexities of fibromyalgia , including chronic inflammation, risk factors, and the role of mitochondria, mast cells, microglia, and the brain.
A recent clinical trial sought to investigate the effects of CoQ10 supplementation on serotonin levels and depressive symptoms in patients with fibromyalgia.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is widely distributed throughout the central nervous system (CNS) and is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Reduced GABA levels, or impaired GABA function, in the brain has been linked to psychiatric and neurological disorders including anxiety, depression, insomnia and epilepsy.
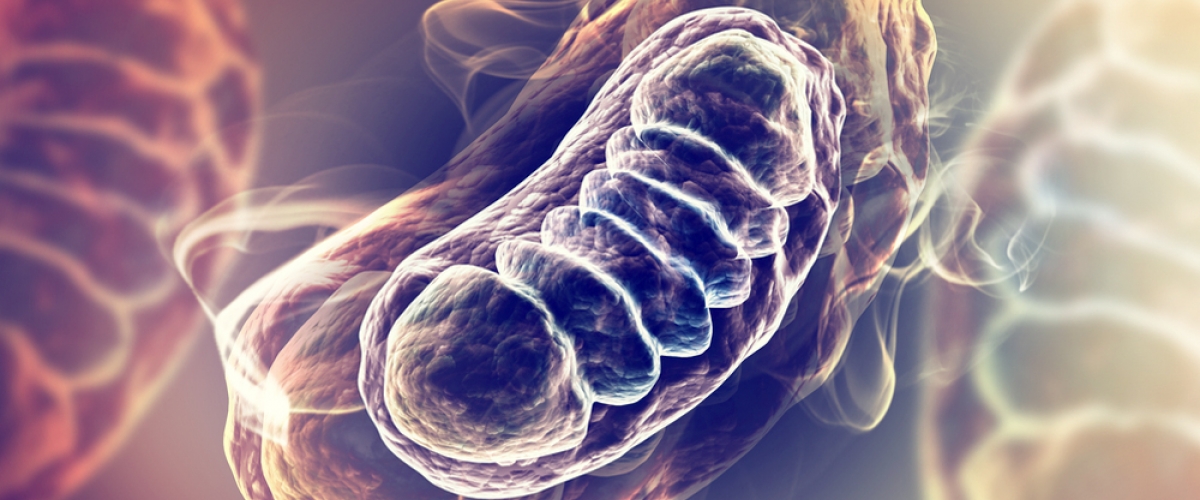
CoQ10 is a well-known antioxidant, active in every cell of the body. It has a strong link with cellular mitochondria and may also have a crucial role in mitochondrial homeostasis and therefore down-regulation of inflammasomes.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a lipid-soluble molecule distributed in all cellular membranes of the human body. It is generally referred to as ubiquinone, due to its ubiquitous, omnipresent nature, and has been used as a therapeutic supplement for more than 30 years.